Combination of gut microbiota and plasma amyloid-β as a potential index for identifying preclinical Alzheimer's disease: a cross-sectional analysis from the SILCODE study
Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid-β; Gut microbiota; Plasma;阿尔兹海默症;淀粉样蛋白β;胃微生物群;- Alzheimers Res Ther
- 2022
- 7.6
- Human
- MSD
- 神经系统
- venous blood
- 神经系统
- 阿尔兹海默症
- Aβ40,Aβ42
- doi: 10.1186/s13195-022-00977-x.
Abstract
MSD技术在阿尔茨海默症和帕金森中的应用
肠道菌群与血浆淀粉样蛋白-β一起作为鉴别临床前阿尔茨海默病的指标
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种起病隐匿的进行性发展的神经系统退行性疾病。由于缺乏有效的策略来延缓或防止AD的发展,那么就采取干预措施针对AD的临床前阶段可能是最好的治疗成功的机会。越来越多的研究结果支持肠道菌群具有调节大脑功能的潜力,如记忆和学习。本研究肠道菌群与血浆淀粉样蛋白-β一起作为潜在的鉴别临床前阿尔茨海默病的指标。

本研究招募了34名A β阴性认知正常(CN−)参与者、32名A β阳性认知正常(CN+)参与者和22名认知障碍(CI)患者,包括11名轻度认知障碍(MCI)患者和11名AD痴呆患者作为本研究的对象。Meso Scale Discovery (MSD)电化学发光技术用来检测CN− 和CN+参与者血浆中A β40,A β42的含量。
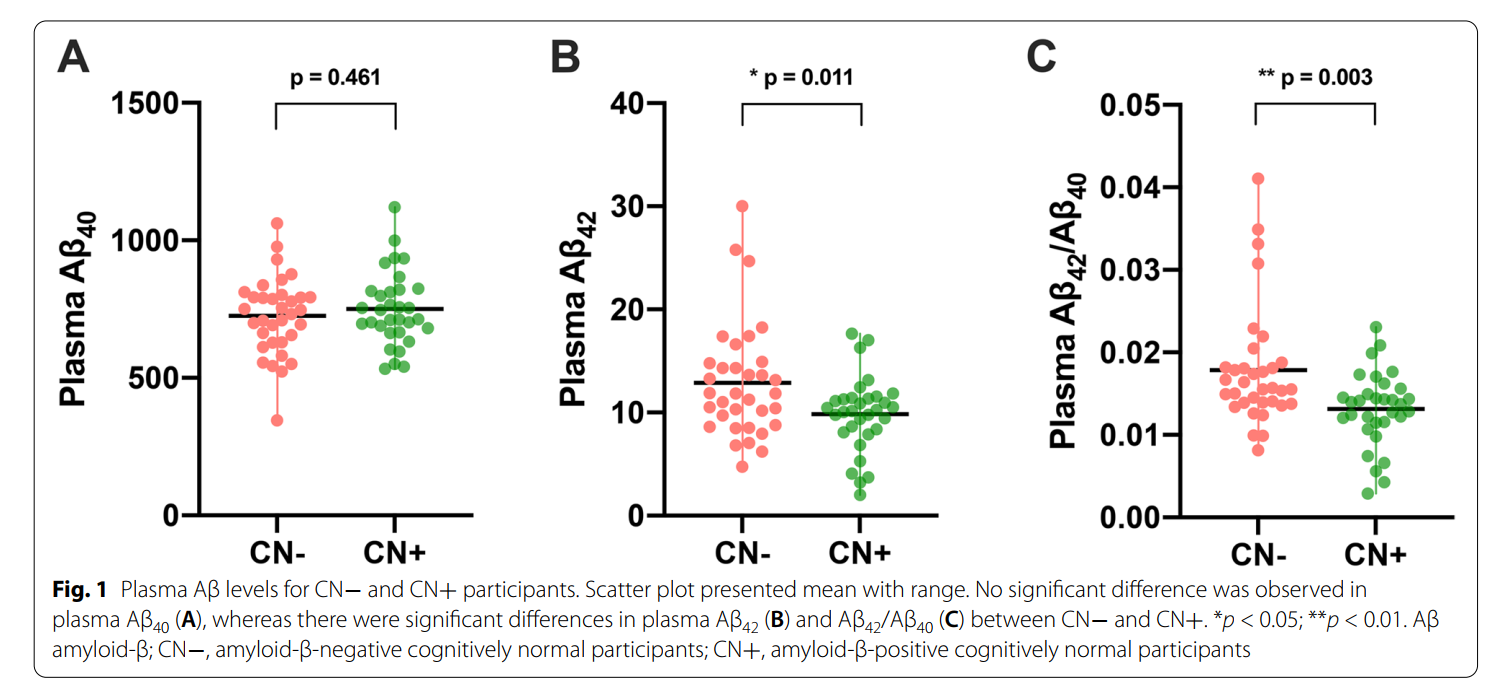
与CN−组相比,CN+组血浆A β42明显降低
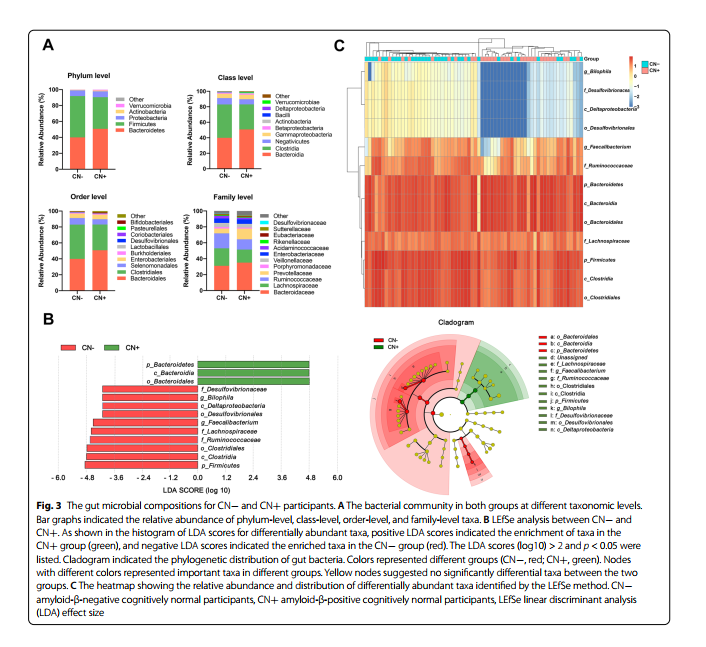
CN+与CN−参与者的主要的肠道微生物基本一致,利用LEfSe分析确定CN+参与者的不同微生物区系。结果表明CN+组的拟杆菌门、拟杆菌纲、拟杆菌目相对丰度显著富集, 而厚壁菌门、梭菌纲含量明显减少。文章发现了厚壁菌门梭菌纲、梭菌目、梭菌科、瘤胃球菌科、从CN−开始逐渐减少到CN+和CI。
使用ROC分析方法,我们首先估计了每个血浆Aβ标记在识别CN+和CN -个体时的鉴别能力。血浆Aβ42/ Aβ40的鉴别能力较好,其次是血浆Aβ42
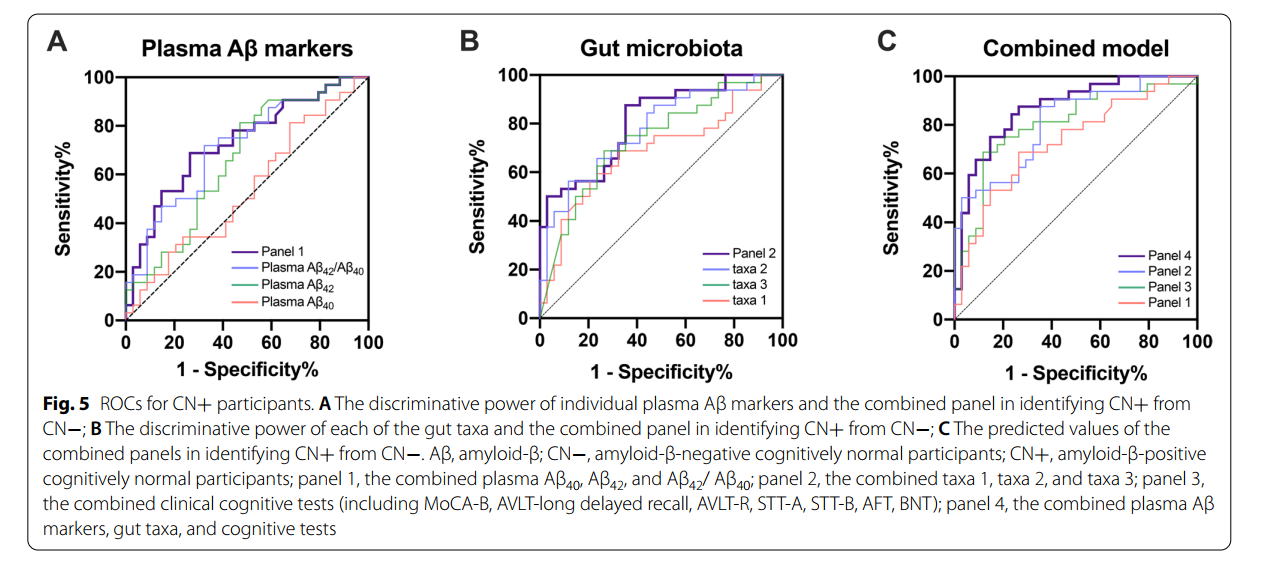
综上所述,研究结果证实了肠道菌群与血浆Aβ42/Aβ40可作为临床前AD的筛选工具而针对肠道菌群可能会为AD相关认知功能下降的治疗策略提供新的思路。
快速眼动睡眠障碍中SNCA低甲基化是一种帕金森病的潜在生物标志物
α-synuclein与帕金森病(PD)的发病机制有关,但在特发性快速眼动睡眠行为障碍(iRBD)中的研究还不透彻。本研究纳入30例iRBD患者,30例PD患者,以及30例年龄和性别匹配的健康对照(HC)。α-synuclein蛋白水平采用MSD方法测量。

在本研究中,研究了α-synuclein在遗传和蛋白水平上的不同分布,以建立RBD和PD的潜在生物标志物。本研究发现
(1)与HC相比,iRBD 和PD组SNCA的甲基化明显降低;
(2) 与疾病严重程度相关的HC患者相比,PD患者的血浆α-synuclein水平升高;
(3) PD患者中SNCA甲基化水平与血浆外泌体α-synuclein相关;
(4) SNCA甲基化水平和α-synuclein水平与PD发病风险增加相关。
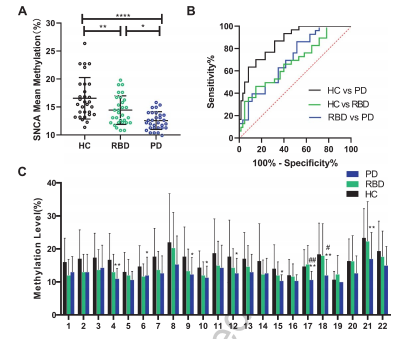
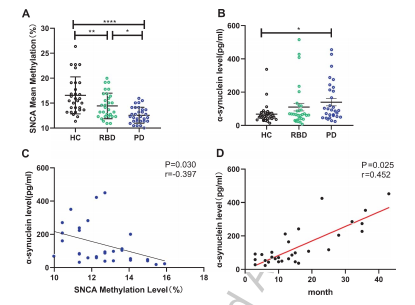

总之,iRBD患者和PD患者白细胞均存在SNCA低甲基化,提示SNCA甲基化可作为PD早期诊断的潜在生物标志物。
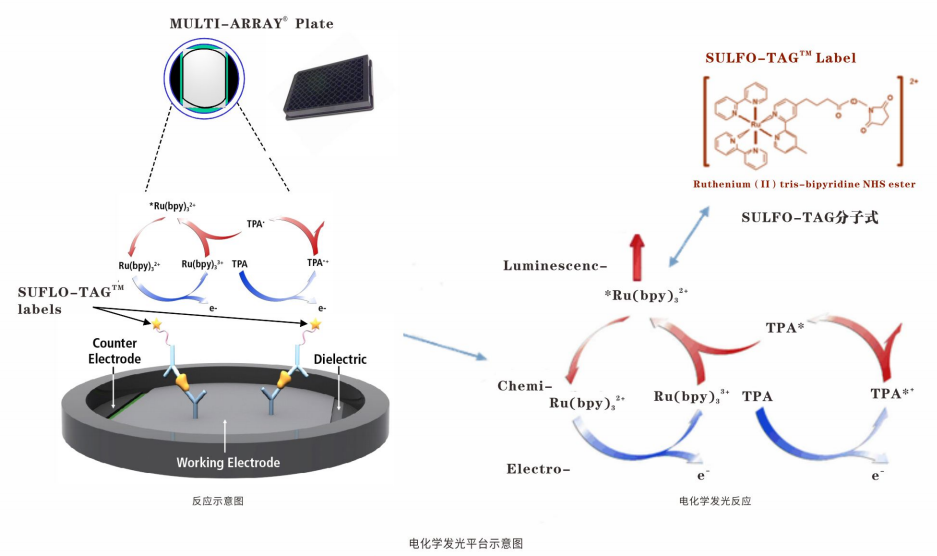
以上两篇文章中都有用到MSD电化学发光技术,该技术是基于ELISA基本原理的升级,在板底通电从而激发标记物SULFO-TAG发光并由CCDCamera进行信号采集;MSD ECL技术大大提高免疫分析的灵敏度,延伸了线性范围。MSD通 过点阵技术,在96孔石墨电极板里可实现10个指标/每孔的检测,同时实现多个指标的相对或绝对定量。
MSD电化学发光技术独具一格的“ 六合一”特点:
亚fg/ml灵敏度,低背景,多靶点检测,6个数量级线性范围,适用于不同样本基质 ( 血清/血浆, 细胞培养上清,脑脊液,尿液,组织匀浆,细胞裂解液)(人/猴子/小鼠/大鼠),5-25ul微量样本检测。
LabEx作为多因子实验服务专家,可以提供MSD/Luminex/CBA等多因子检测服务,速度快,质量高,服务更专业。LabEx每年检测25万+多因子样本,并可提供专业的生物信息学分析,以帮助用户获得更高质量的检出数据和服务体验。此外,LabEx还可以提供以下服务平台:
本网站销售的所有产品及服务均不得用于人类或动物之临床诊断或治疗,仅可用于工业或者科研等非医疗目的。











 沪公网安备31011502400759号
沪公网安备31011502400759号
 营业执照(三证合一)
营业执照(三证合一)


